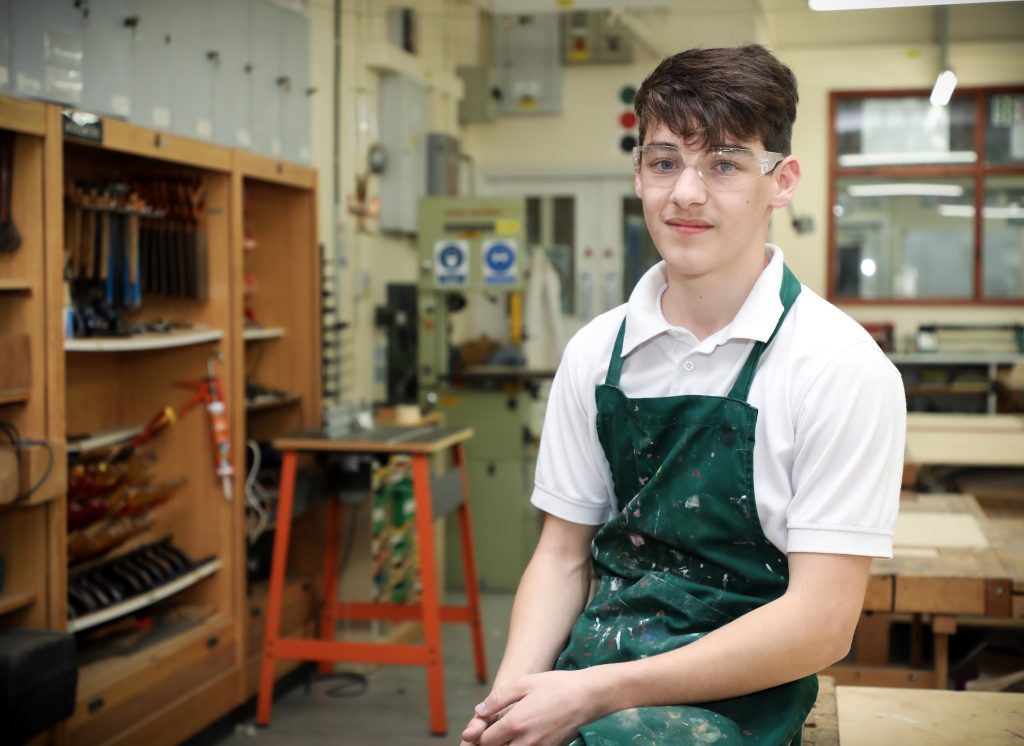
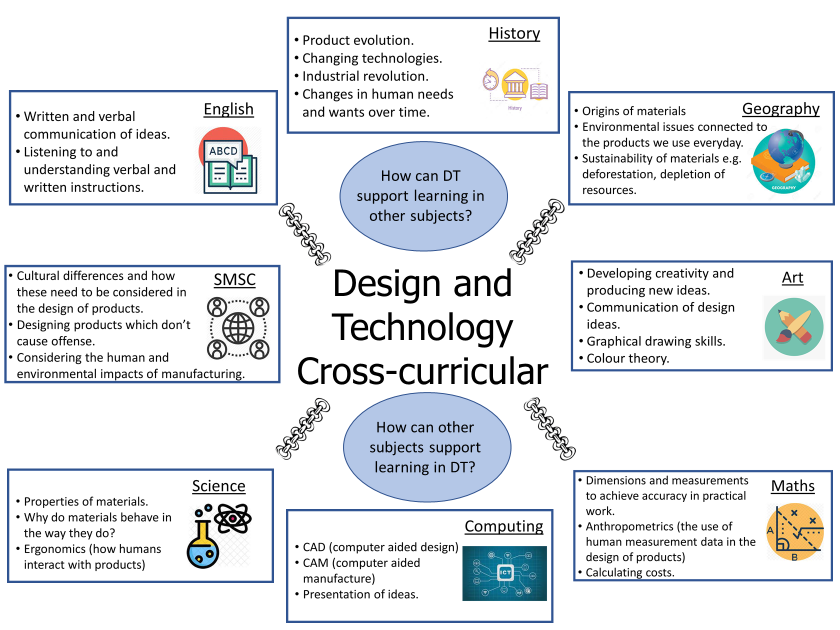
“To create global citizens who can interact with and shape the human world around them by creating problem solvers who blend a range of disciplines to find solutions to the problems our species and the planet faces. Students will become discerning consumers and practical influencers, while protecting and enhancing the natural world.”
What does the national curriculum say?
The national curriculum for design and technology aims to ensure that all pupils develop the creative, technical and practical expertise needed to perform everyday tasks confidently and to participate successfully in an increasingly technological world. They should build and apply a repertoire of knowledge, understanding and skills in order to design and make high-quality prototypes and products for a wide range of users. They should be able to critique, evaluate and test their ideas and products and the work of others.
KS3
|
Through a variety of creative and practical activities, pupils should be taught the knowledge, understanding and skills needed to engage in an iterative process of designing and making. They should work in a range of domestic and local contexts [for example, the home, health, leisure and culture], and industrial contexts [for example, engineering, manufacturing, construction, food, energy, agriculture (including horticulture) and fashion]. The materials they will work with are – timbers, metals, papers & boards, polymers, systems & control and textiles. Link to full document here |
|
Curriculum USP |
|
Year 7 Unit 1: Desk Tidy Materials focus area (s): Polymers, timbers
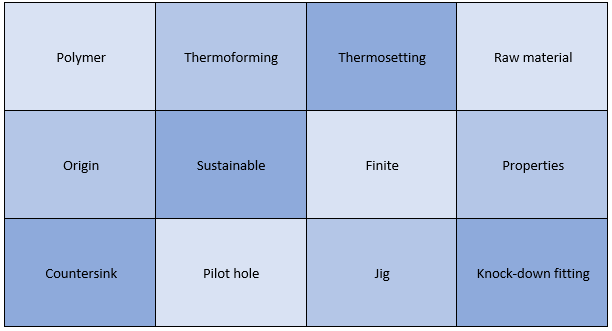
In this unit, pupils will be introduced to the workshop and learn basic workshop skills through the manufacture of a desk tidy. This unit will focus on workshop health and safety procedures whilst developing skills in shaping, drilling, sanding and finishing materials. Students will learn about the classification and properties of thermoforming and thermosetting polymers. |
|
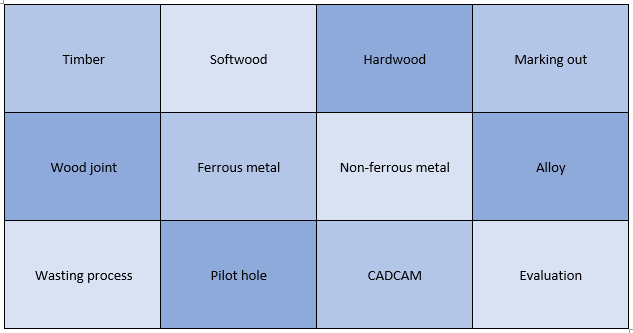
Year 7 Unit 2: Wind Chimes Material focus area (s): Metals, timbers
In this unit, students will be manufacturing a set of wind chimes inspired by the work of the artist, Keith Haring. They will devise their own success criteria for the wind chimes which they will then use to evaluate their finished product. Students will be introduced to the benefits of using CADCAM in the design and manufacture of products. |
|
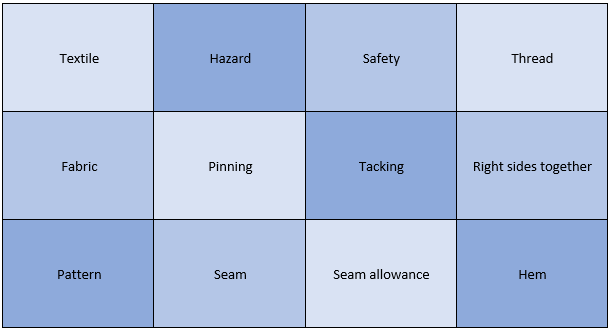
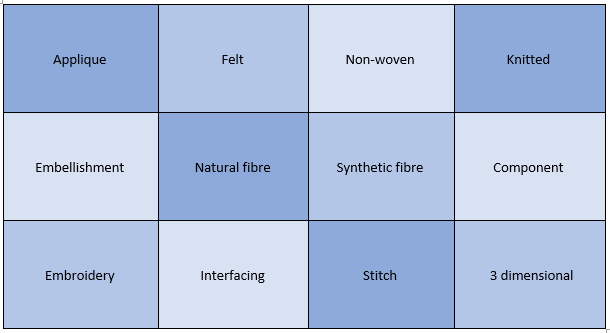
Year 7 Unit 3: Beanbag Chicken Material focus area (s): Textiles In this unit, students will be introduced to textiles. They will learn about the origins of a range of natural and synthetic fibres and how these are made into yarns and fabrics. We will consider how fibre properties can be exploited to create the vast range of textile products we use every day. Students will learn basic sewing skills of pinning and tacking and will be taught to use the sewing machine. They will manufacture a small beanbag toy to practice and demonstrate these skills. |
|
Year 7 Unit 4: Block Bots Material focus area (s): Timbers, polymers
In this unit, students will design and manufacture a Block Bot. They will learn how to use a design brief and research to write a design specification which they will have to follow when producing design ideas. They will build on their skills using CAD software by designing a character and outfit for their Block Bot which can be cut using the laser cutter. They will also continue to develop practical workshop skills as they manufacture the component parts of the product. |
|
Year 7 Unit 5: Tie Dye Cushion Material focus area (s): Textiles
In this unit, students will be learning about the process of dyeing fabrics. They will have the opportunity to make some natural dyes and compare them to synthetic dyes. They will explore some of the sustainability concerns surrounding the manufacture of textile products and how the wet processing stages of manufacture contribute to environmental damage. The practical element for this unit will be to make a tie-dyed cushion, where students can decide whether to use natural or synthetic dye. |
|
Year 7 Unit 6: Steady Hand Game Material focus area (s): Systems & Control
In this unit, students will be designing and manufacturing a steady hand game. They will learn how to build a simple electronic circuit, incorporating different components along with how to test a circuit. They will also learn how to draw a circuit and the standard symbols which are used for components. Students will put their learning into practice by manufacturing a modern art inspired steady hand game. |
Year 8
|
Year 8 Unit 1: Design Movement Clock Materials focus area (s): Timbers, Polymers
In this unit, pupils will be designing and manufacturing a clock inspired by a design movement of the 20th century. This unit gives students a taste of how products are manufactured in industry; from design brief through to final product and how product ranges are designed. They will learn how to analyse a design brief, conduct research and use this information to write a design specification. |
|
Year 8 Unit 2: Food cushions Materials focus area (s): Textiles In this unit students will demonstrate their creativity by designing and making a cushion in the shape of a food product. They will learn how to produce a pattern and how to manipulate and sew fabric on to produce a 3d shape. They will explore a range of ways to colour and embellish fabrics such as applique, embroidery, printing and beading and will select appropriate techniques to use in their design. |
|
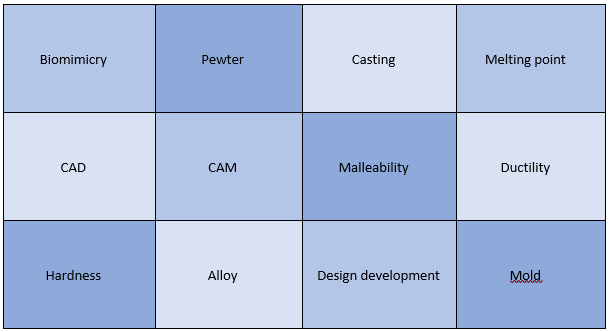
Year 8 Unit 3: Pewter Casting Materials focus area (s): Metals In this unit, students will design and make a piece of pewter jewellery. They will build upon knowledge of metals and alloys from year 7 and explore the properties of metals which determine their uses. They will use CAD to create a design inspired by biomimicry and use this to produce a mold into which they will cast molten pewter. Students will learn about finishing techniques such as filing, buffing and polishing required to make a usable product. |
|
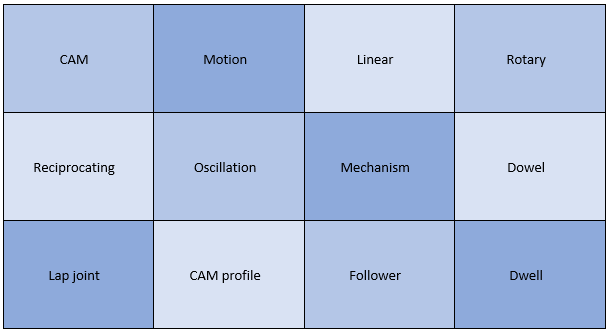
Year 8 Unit 4: CAM Toy Materials focus area (s): Timbers, Systems & Control In this unit, students will design and make a CAM toy. They will learn about the different types of motion and how CAMs can be used to produce movement. They will demonstrate their learning by designing a CAM toy which makes use of at least one type of CAM. Prior to manufacturing their product from timber, they will test their design through modelling and consider the value doing this in developing a design. |
|
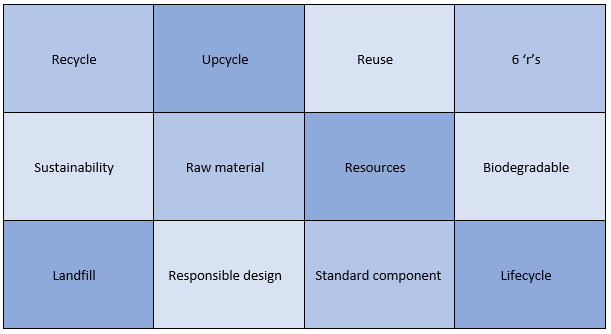
Year 8 Unit 5: Upcycled Lamp Materials focus area (s): Timbers, Systems & Control, Metals In this unit, students will learn about some of the sustainability issues that designers today face. They will investigate product lifecycle’s; from raw material to end of life. They will learn about the 6 ‘r’s of sustainability and how we can refer to these when considering whether to purchase new products. To demonstrate their learning, the practical element for this unit will be to manufacture an upcycled USB lamp, made from waste food tins from our food lessons. |
|
Year 8 Unit 6: Photochromic Bag Materials focus area (s): Textiles In this unit, students will design and make a bag which has a photochromic motif. They will learn about smart materials and their use in both functional and decorative applications. Students will create their own fabric by producing Zentangle art work which they will apply to the fabric with batik. They will then stencil a design onto the fabric which they will paint in colour-changing photochromic ink. They will use their fabric to make into a bag design of their choice. |
|
**Year 9 will cover 5 slightly longer units which reflect the increase in complexity of practical work**
Year 9 Unit 1: Quiet Book for Dhekelia Early Years Materials focus area (s): Textiles In this unit, students will have the opportunity to experience how designers work in the real world by designing a product for a client. They will be working with Dhekelia Early Years to design and make a Quiet Book which can be used by the children at the setting. Our students will have to ensure their designs meet the strict requirements of the Early Years staff, considering how their product will be educational and engaging but most importantly, safe to use. Each student will design and make a page of the book using textile materials, which will be assembled as a complete book to present to the Early Years children. |
|
Year 9 Unit 2: Tealight Holder Materials focus area (s): Timbers In this unit, students will design and make a wooden tealight holder inspired by a culture of their choice. They will learn how to produce simplified design motifs from images from their research. They will learn how to draw these in 2D Design software to produce a suitable design to be cut into wood using the laser cutter. This unit will also cover the branding and packaging of products. Students will use this learning to produce suitable packaging for their product. |
|
Year 9 Unit 4: Bird Box/Bee Hotel Materials focus area (s): Timbers In this unit, students will design and make a bird box or bee hotel. They will have to carefully research the requirements of this type of product so it is fit for purpose and will last in its intended environment. Students will learn about properties of materials and how material finishes can be used to improve their properties. We hope to install a webcam into two of the bird boxes to see if we can capture any birds nesting. |
|
|
Year 9 Unit 5: Printed Lunch Bag Materials focus area (s): Textiles In this unit, students will design and make a reusable lunch bag. They will revisit the topic of sustainability from year 8 and analyse current lunch packaging solutions. They will learn about how composite fabrics are created and how this changes properties of materials. Students apply this learning by creating a repeat pattern which they will print onto fabric which they will then layer with insulating wadding and laminate with vinyl. They will make their laminated fabric into a reusable lunch bag. Students will also learn about how composite materials create their own problems in terms of sustainability, and how we can weigh up the advantages and disadvantages of these materials. |
|
Edexcel GCSE 9-1 Design and Technology
The GCSE in Design and Technology enables students to understand and apply iterative design processes through which they explore, create and evaluate a range of outcomes. The qualification enables students to use creativity and imagination to design and make prototypes (together with evidence of modelling to develop and prove product concept and function) that solve real and relevant problems, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. It gives students opportunities to apply knowledge from other disciplines, including mathematics, science, art and design, computing and the humanities. Students will acquire subject knowledge in design and technology that builds on Key Stage 3, incorporating knowledge and understanding of different materials and manufacturing processes in order to design and make, with confidence, prototypes in response to issues, needs, problems and opportunities. Students learn how to take design risks, helping them to become resourceful, innovative and enterprising citizens. They should develop an awareness of practices from the creative, engineering and manufacturing industries. Through the critique of the outcomes of design and technology activity, both historic and present day, students should develop an understanding of its impact on daily life and the wider world and understand that high-quality design and technology is important to the creativity, culture, sustainability, wealth and wellbeing of the nation and the global community. |
|
Course structure: Year 10 Year 10 is spent studying the both the core content and chosen specialist material area through a mixture of theory and practical work. Practical work could include product analysis, product disassembly, focused practical tasks and full design and make project work. The practical work will enable students to develop the skills they will need to complete their NEA in year 11. Year 10 Projects include:
|
Year 11 |
| NEA (Non-Exam Assessment) |
|
Non-examined assessment 50% of qualification 100 marks Content overview: 1 – Investigate (16 marks) This includes investigation of needs and research, and a product specification 2 – Design (42 marks) This includes producing different design ideas, review of initial ideas, development of design ideas into a chosen design, communication of design ideas and review of the chosen design 3 – Make (36 marks) This includes manufacture, and quality and accuracy 4 – Evaluate (6 marks) This includes testing and evaluation Students will undertake a project based on a contextual challenge released by the exam board. The project will test students’ skills in investigating, design making and evaluating a prototype of a product. They will produce a prototype product and supporting written portfolio. Example contextual challenge: Going to the Zoo |
|
|
|
Written examination (1hour and 45 minutes) 100 marks 50% of GCSE Content overview: 1 – Core content and any one from the following materials categories: 2 – metals 3 – papers and boards 4 – Polymers 5 – systems and control 6 – textiles 7 – timbers The paper consists of 2 sections. Section A is assessed on the core content and Section B is assessed on the material category students have chosen. Section A: Core This section is 40 marks and contains a mixture of different question styles, including open-response, graphical, calculation and extended open-response questions. There will be 10 marks of calculation questions in section A. Section B: Materials categories This section is 60 marks and contains a mixture of different question styles, including open-response, graphical, calculation and extended open-response questions. There will be 5 marks of calculation questions in Section B. More information and the full specification can be found here |
|
|
A Level Design and Technology Product Design (AQA) |
|
A level Design and Technology: Product Design requires students to engage in both practical and theoretical study. This creative and thought-provoking qualification gives students the practical skills, theoretical knowledge and confidence to succeed in a number of careers. Especially those in the creative industries. They will investigate historical, social, cultural, environmental and economic influences on design and technology, whilst enjoying opportunities to put their learning into practice by producing prototypes of their choice. Students will gain a real understanding of what it means to be a designer, alongside the knowledge and skills sought by higher education and employers. |
| NEA (Non-Exam Assessment) |
|
What’s assessed? Practical application of technical principles, designing and making principles. How it’s assessed
Evidence Written or digital design portfolio and photographic evidence of final prototype. |
| Written Examinations x 2(Externally assessed) |
|
Paper 1 What’s assessed? Technical principles How it’s assessed Written examination (2 hours and 30 minutes) 120 marks 30% of A level Questions Mixture of short answer and extended response questions. Paper 2 What’s assessed? Designing and making principles How it’s assessed Written examination (1 hour and 30 minutes) 80 marks 20% of A level Questions Mixture of short answer and extended response questions. Section A:
Section B:
Mixture of short and extended response questions. More information and the full specification can be found here |
Useful books
|
|
Useful Websites: https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zvg4d2p http://www.julieboyd.co.uk/dt/ https://www.stem.org.uk/home-learning/secondary-design-technology |
|
How it’s made: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLb4Aujw26R6FsJJ3py4ponBlBxp0UnRA |